For decades, the development of the gaming industry has been closely linked with scientific discoveries and novelties in the world of computing technologies. Let’s take a look at how the evolution of engineering impacted the development of the entertainment industry.
The first computer games appeared almost at the same time as the first computers, in the 1930-1940s. And certain entertainment devices - such as a rocket simulator - were developed even before the creation of the first computer.
For decades, the development of the gaming industry has been closely linked with scientific discoveries and novelties in the world of computing technologies. It’s worth noting that not only do other industries offer new ideas and solutions for the entertainment industry - games can also work for the good of mankind. Certain large-scale projects, like the Unix operating system, initially started out as game developments.
The history of gaming has experienced a lot of ups and downs, mostly because new games suddenly became popular, or, alternatively, a creative crisis launched a financial crisis in the industry. For example, the decline in the computer game market in 1983 was caused by an influx of console-based games which were extremely similar to each other and stopped attracting users.
With the development of computing technology, improvements in metal manufacturing, and emergence of 3D graphics, games became more and more captivating, but also more difficult to develop.
The computer gaming industry emerged in the mid-1970s. Since then, the market has been actively developing, attracting growing numbers of talented developers to create games, investments to transform ideas into reality, and of course, the players themselves, whose opinions decided the success or failure of a new release.
Game development has always been tightly linked with technological progress. As soon as a new technology was discovered, developers rushed to implement it in their latest game.
Let’s take a look at how the evolution of engineering impacted the development of the entertainment industry.
Electronic games
Some gaming consoles were developed even before the invention of computers and worked based on analog elements. Engineers working in computer labs built entertainment consoles out of the parts that they used in their research and for other developments.
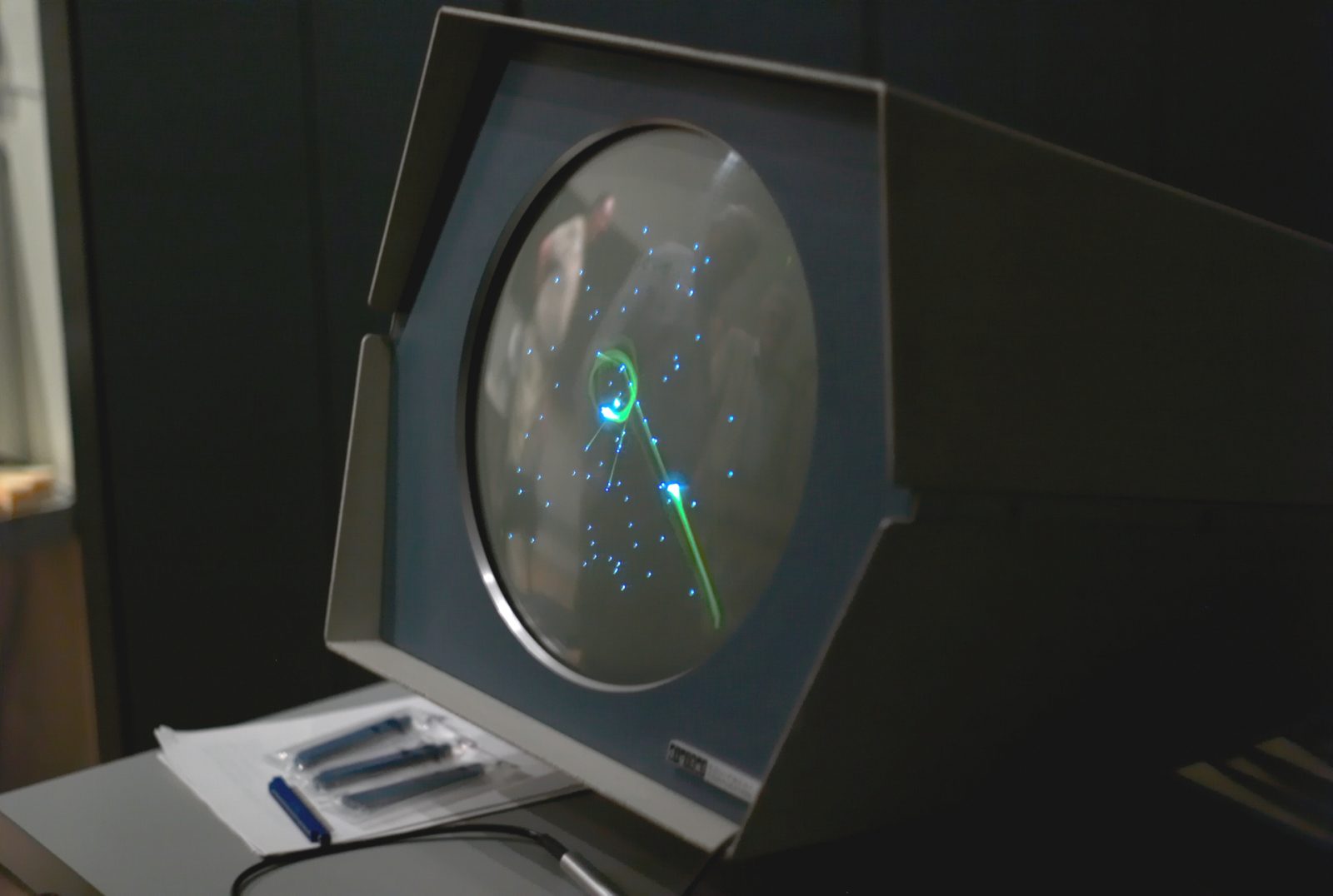
In 1947, the first rocket simulator was created. It was made up of an oscilloscope, a cathode ray tube and some control elements. This simulator later inspired developers who created popular video games like Spacewar! and Computer Space.
In 1958, the famous Tennis for Two game was created, consisting of an oscilloscope and an analog computer. Engineers from the Brookhaven National Laboratory created it to entertain visitors with a game of virtual tennis. However, just a year later, the console had to be taken apart, because the computer and oscilloscope were needed for other more important projects.
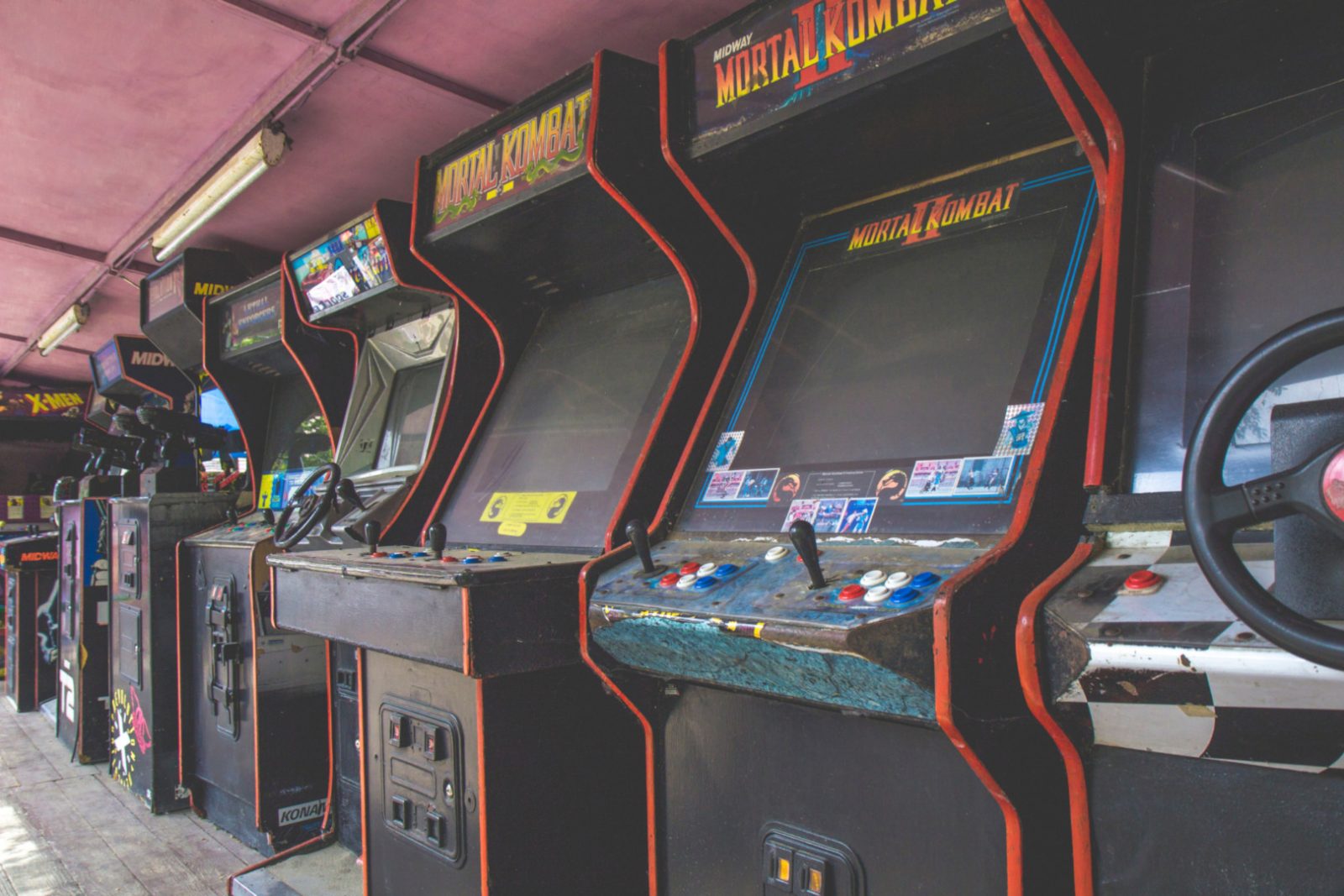
Arcade games
Before the invention of personal computers, arcade games were very popular. They usually looked like large stands with mounted displays, control panels and coin slots. Inside, the stands were equipped with circuit boards, which represented the hardware of the game. Usually, the external appearance of the stand matched the content of the game. Stands could be vertical or horizontal, with certain simulators built like the interior of a car or a plane.
Because arcade game stands were rather expensive, their owners were supposed to pay off their losses by inviting players. That’s why these games were usually placed in bars or specialized gaming clubs.
With the emergence of PC games, a lot of arcade games lost their profitability. Their owners could only rely on consoles that required special equipment. For example, racing games equipped with pedals and steering wheels, or shooters with physical guns. Dancing arcade games became particularly popular.
Game consoles
Game consoles appeared in the 1970s and remain popular today. Modern gamers are already playing on eighth-generation game consoles.
Consoles initially offered a compact solution for at-home gaming. The need for special hardware (joystick, gamepad) to control the game created a business model where both games and consoles became tightly linked within a single ecosystem. If you had a console, you had to buy new games that were compatible with it, while users who wanted to play a particular game had to buy a console.
The history of at-home game consoles started with models like Magnavox Odyssey. Today’s market leaders are Xbox, Nintendo and PlayStation.
At the outset, games for consoles were sold in physical format - on special cards, magnet or optical devices. Today, manufacturers are gradually transitioning to an online shopping system, even though most games are still being sold on Blu-ray discs.
Regular smartphones are slowly becoming game consoles as well. Additional gadgets like small gamepads or joysticks can transform a phone into a full-fledged game console. What’s more, with this option you can hold both the control panel and the screen in your hands, similarly to PlayStation Portable (PSP).
The era of personal computers
With the advent of personal computers, many popular games were ported to be used on these new machines.
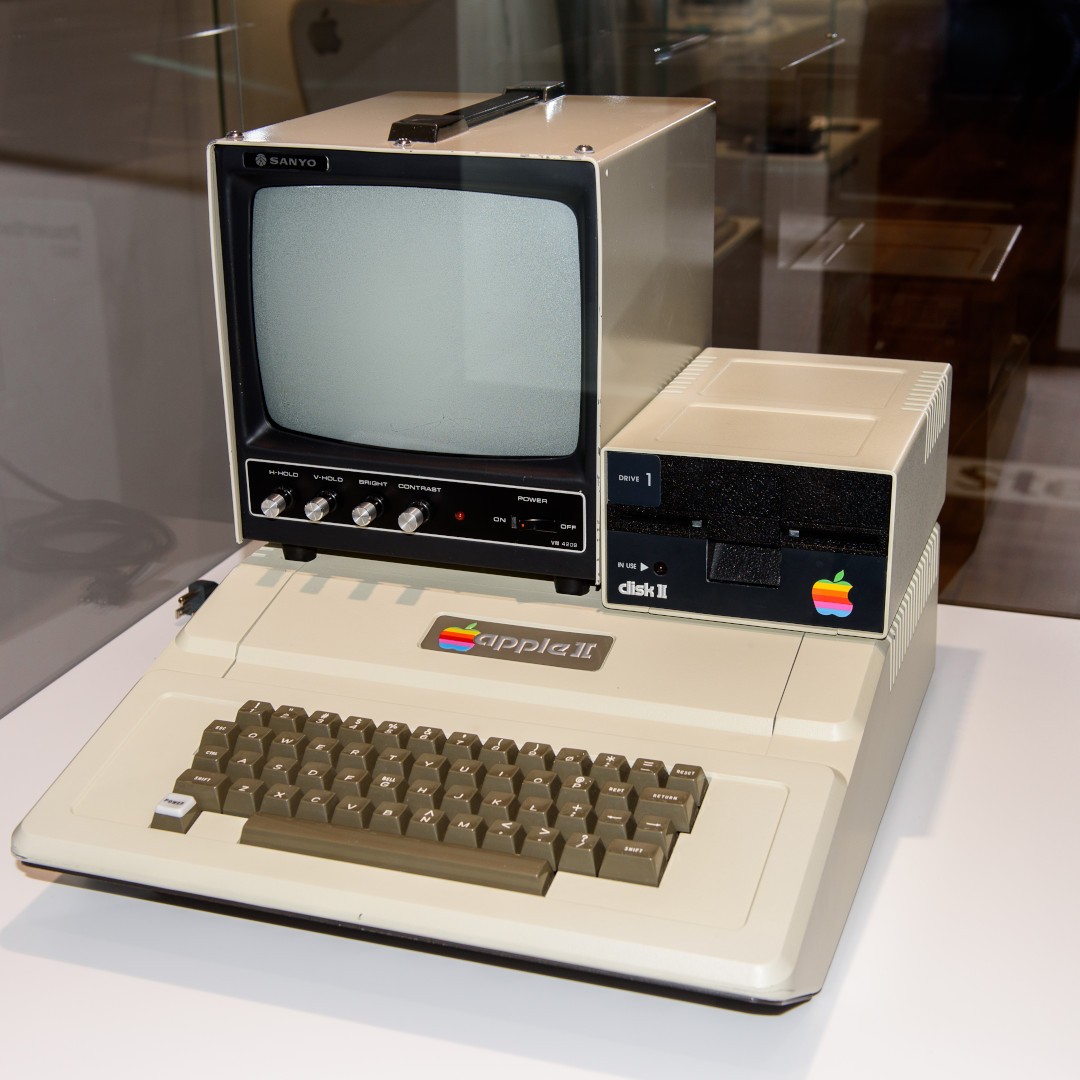
In 1977, Apple presented Apple II, the company’s first serial computer and one of the first successful personal computers in the world. This device became popular for both office and personal work. Apple II was the first computer that inspired the creation of graphic commercial games.
Later, the widespread adoption of PCs in the 1990s and 2000s led to a surge in popularity for games created specifically for at-home use on personal computers.
Today, most games are manufactured either for Windows and OS X systems (personal computers), or for mobile platforms.
3D graphics
The very first games either had simple two-dimensional graphics or were text-based. With the invention of 3D graphics, developers started competing for realism. Gradually, game manufacturers started aiming to recreate the quality of special effects and graphics used in movies. However, no one has managed to fully attain the standards set by Hollywood studios, even today. In games, all elements are created in real-time, which sets limitations on productivity and time. When movies are shot, the images can always be improved by allocating more time for processing.
With the emergence of 3D graphics, a new chapter was launched in the game development industry. Gradually, developers transitioned to making characters and locations look more natural.
Before processors became more powerful, it was practically impossible to create detailed images. But by the mid-1990s, special graphic processors were created, used exclusively for computing images and significantly decreasing the central processor workload.
The development of 3D graphics eventually created new instruments for building realistic textures, computing physical characteristics and enabling in-game interactions between objects.
3D games became a fan favourite: captivating special effects and well-designed realistic details allowed players to completely immerse themselves in the game.
The Internet
The emergence and widespread adoption of the Internet gave an enormous push to the development of online multiplayer games.
Even the first consoles offered two-player options, with the later emergence of games like Doom which allowed players to engage with others through a local network. But full-fledged development of online games was only made possible by the creation of a fast, accessible Internet.
When each home was connected to the Internet, it became possible to create mass multiplayer online games with many thousands of players, such as the games in the Warcraft series or World of Tanks.
Online games
Classic computer games require users to install a separate application on their computers. However, when the Internet became fast enough, many developers switched to online games that allowed users to play directly in their browsers. They only had to visit the game website.
Simplified development led to the creation of a large number of low-quality, poorly drawn games, which were mostly free for users, with manufacturers earning ad revenue. Adobe Flash became a popular program for development of these games. By 2017, it was defeated by HTML5. Adobe admitted that Flash technology had become outdated, announcing that they would cease support of the platform by 2020.
Mobile games
With the widespread adoption of smartphones, developers started creating games across a wide range of genres - from shooters to puzzles - specifically for mobile platforms.
From a technical standpoint, there was a new architecture, as well as new control methods, like sensor inputs and gyroscopes. Thus, manufacturers of entertainment apps ported existing, familiar playing worlds, but also started actively developing new games adapted to mobile phones.
Modern smartphones based on iOS or Android offer a wide range of games for their users: from countless puzzles, adaptations of tetris and games like 2048, to full-fledged shooters, arcade tank simulators and bestselling hits like Angry Birds and Fruit Ninja.
In recent years, there’s been a significant increase in mobile games with augmented reality support, and additional gadgets can transform mobile phones into next-generation game consoles.
AR and VR
Augmented and virtual reality technologies are actively being integrated into various areas: from advertising and entertainment to scientific research and medicine. Most tech giants have contributed their efforts to the new market as manufacturers of specialized equipment and software.
However, environment building and simulation technologies are currently finding the most applications in the gaming industry. It’s easy to jump to the disheartening conclusion that AR and VR are only applicable in entertainment. In reality, there’s no reason for such pessimism. The main reason for this trend is that other industries - such as science - require much more rigorous development and testing processes for complex technologies like these. Only a few years down the line, AR and VR game developers might already have enough experience that can be applied in other areas as well.
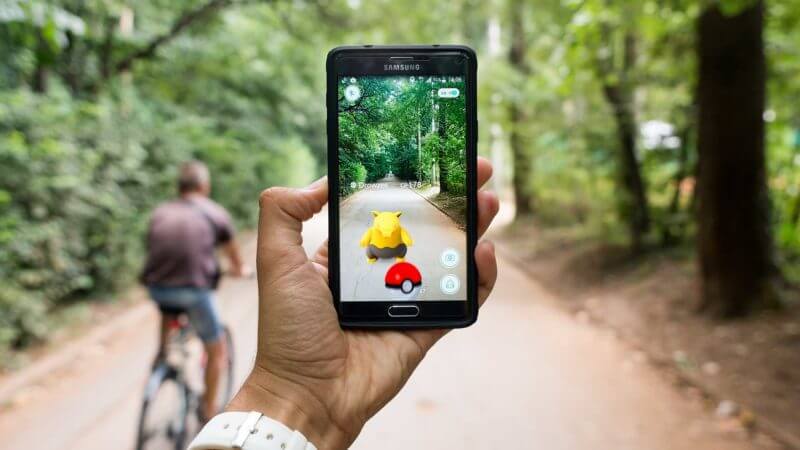
One of the most popular AR games, Pokémon Go, has attracted the attention of over 100 million players around the world, bringing hundreds of millions to its creators.
Artificial intelligence
At the formative stages of the gaming industry, with the emergence of the first non-commercial, relatively simple computer games, developers were faced with the question: how can they transform the computer into an opponent capable of playing at the level of a human?
One of the first algorithms that allowed users to play against their computer was OXO, a program for tic-tac-toe. Chess programs formed a separate field, becoming ever more advanced over the decades, before finally beating the world’s best chess players.
Today, artificial intelligence technology enables programmers to build algorithms capable of learning based on large data sets. These algorithms are gaining wide applications in gaming. They allow developers to build more realistic locations and significantly improve game logic.
Blockchain
The explosive growth in the popularity of blockchain technology has affected the gaming industry as well.
One of the key advantages of blockchain games is the option of creating a system of in-game rewards and payments. Users can buy products and receive rewards for activity.
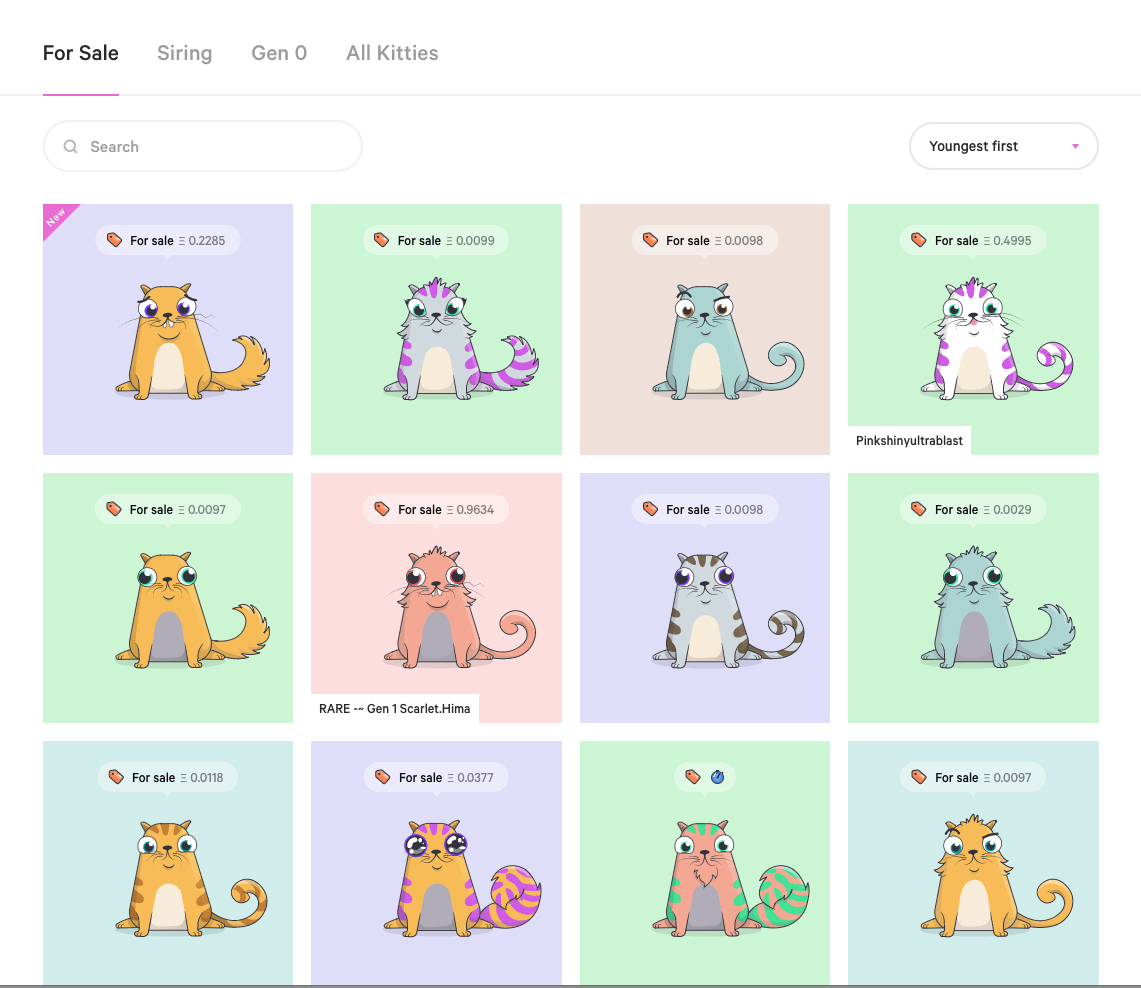
The most popular blockchain game, Cryptokitties, made waves in the crypto community. Certain virtual pets were sold for tens of thousands of dollars, while the Ethereum network (which served as a basis for the game) was overloaded due to a large transaction volume at one point.
The future of computer games
Future development of the gaming industry will likely move towards even greater integration with the real world. There will be more global AR games and gadgets offering complete immersion into virtual gaming worlds.
Developers will undoubtedly aim to use any new technology to make games more interesting and captivating. As soon as the first full-fledged quantum computers are released, developers are sure to create games for them as well.
Share this with your friends!














Be the first to comment
Please log in to comment