The Japanese broadcaster NHK launched the first ultra-high definition channel with an 8K resolution on December 1st, 2018. Available only to a limited number of viewers in Tokyo, the new broadcast format...
The Japanese broadcaster NHK launched the first ultra-high definition channel with an 8K resolution on December 1st, 2018. Available only to a limited number of viewers in Tokyo, the new broadcast format supports a resolution of 7680×4320 pixels, a speed up to 120 frames per second, and 22.2-channel sound with a maximum bandwidth of 6600 Mbps. Viewers will need a satellite receiver and a TV that supports 8K to view the broadcasts.
What does this news mean for ordinary viewers? In short, we barely had time to get used to 4K and learned to smile condescendingly at the mention of Full HD, as they are being replaced by a new format with an even larger screen resolution. In Full HD it is 1920×1080 pixels, and in 4K — 4096×2160.
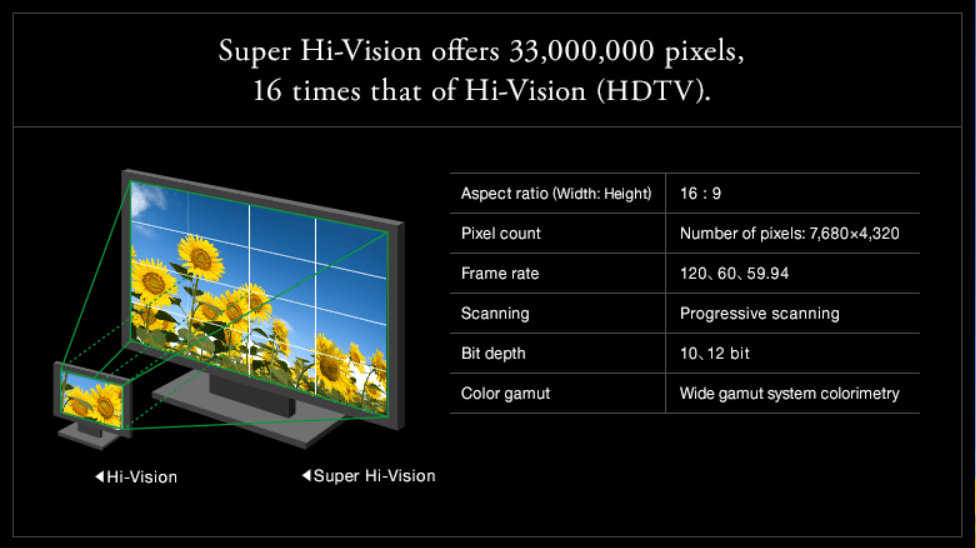 Image source: http://www.nhk.or.jp/8k/index_e.html
Image source: http://www.nhk.or.jp/8k/index_e.htmlIt doesn’t exist if it’s not on TV
So, what is 8K format and why is it called that? No, you didn’t miss the appearance of 5, 6, or 7K — they never appeared. That is, computer monitors with a 5K resolution can not only be found, but also bought. But for digital television and cinema intermediate formats between 4K and 8K do not exist.
8K is called so because the horizontal image at this resolution has about 8 thousand pixels. The format, patented by NHK in 2012 as 8K Super Hi-Vision, can transmit images at 33.2 million pixels and provides a realistic picture of unsurpassed clarity. 8K has its own encoding, bit rate, sound quality, and color depth. In other words, this is a separate technology, strong signal quality requirements, and relevant content.
 Image source: http://www.nhk.or.jp/8k/index_e.html
Image source: http://www.nhk.or.jp/8k/index_e.html The biggest problem with the new format is the content. Despite how good it is, no matter how much it promises to immerse you in reality, there’s practically nothing available to watch in 8K.
Many film companies released remastered versions of famous films in a higher resolution in the 4K format and new 4K cinemas opened around the world. With 8K, the situation is quite different: officially, only two classic pictures are suitable for viewing — «Space Odyssey» and «My Fair Lady».
Size matters even more
Experts say that the 8K format is generally a format of large, if not huge, screens. When the diagonal is less than 65 inches, the difference in image quality is almost invisible. It becomes noticeable only on a screen starting at 85 inches. The emergence of such giant screens has spurred the development of formats with higher resolution.
No one wants to watch TV through a magnifying glass, everyone needs more and more. According to the forecasts of a leading research firm, IHS Markit, the market for TV’s with a diagonal screen of 75 inches will double by 2020.
And words like «new model», «super image», and «mega resolution» help to increase sales. And it does not matter that 8K is a special technology that must have certain conditions, such as several HDMI 2.0 cables and a separate one for audio transmission. People like to buy numbers, but they don’t really like to think and compare figures with facts. And marketers are well aware of this.
Battle of the two yokozun; Or in Korean — Battle of the Giants
It’s time to talk about the price tag. The latest Samsung TV with support for 8K resolution costs about 9 million rubles. But they alone can solve the problem of lack of content. After all, it’s not possible that Koreans will not invent anything of their own for the latest Japanese invention. The fact is that the Korean giant has prudently developed a technology that allows new TV’s to independently convert images of any resolution to 8K. Whether it’s streaming images, a game console, HDMI input, USB drive, or a mobile output.
The artificial intelligence technology, AI Upscaling, can also optimize sound — for example, at key moments of a football match it can increase the excitement of the audience to create the effect of being present. It can independently analyze and process data from scene to scene, allowing viewers to see any movie or TV show in 8K format. And now the need to launch new special satellite television channels using 8K technology is more a question of price than expediency.
8K: the venue cannot be changed
Where else besides TV would we be able to watch in 8K in the very near future? Of course, fans of video games are waiting, with the aim of maximizing the realism of their adventures on the screen. Developers promise that the impressions of the new games will be indistinguishable from real ones.
Dell, SkyWorth, and Chang Hong have already introduced their 8K monitors, but it’s too early to run and buy them. Their cost today is about 300 thousand rubles, and you will still not see in 8K since graphics processors do not have the speed for the new format. They can only use 4K. Peak sales of new monitors are expected no earlier than in a couple of years.
Monitors, televisions, projectors, cameras, virtual reality glasses — are the expected list of devices using 8K technology. With regard to applications, everything here is also more or less predictable: cinema, design, data visualization in medicine, pharmaceuticals, microbiology, molecular physics, nanotechnology, etc.
NHK promises to continue developing the new format to make it more accessible. And when asked if a 16K technology should be expected, the company’s employees answered that 8K is the limit and there will be nothing better. Representatives of the Taiwanese corporation Innolux, who showed the only screen in the world with a resolution of 16K at the Touch Taiwan 2018 exhibition, will most likely disagree with them.
 Image source: https://tech.sina.com.cn/e/2018-12-04/doc-ihmutuec5972055.shtml
Image source: https://tech.sina.com.cn/e/2018-12-04/doc-ihmutuec5972055.shtmlHowever, Innolux has not published the new technology standard and did not name the approximate price or the date of the start of production. And yes, to check whether the exhibition piece could at least show something except a static image at such a huge resolution was impossible: video in 16K format does not yet exist.
Share this with your friends!






Be the first to comment
Please log in to comment